













Easy treatment with expert
24/7 Emergency Available
Advice with Experts
we are dedicated to staying on top of the latest tools and treatments in pain management. As the leading pain management doctor in New York , our goal is to create a friendly and professional atmosphere that you can rely on for all of your healthcare needs. We couldn’t be the office we are without our exceptional staff. They are always assisting patients by providing the information needed to make the right decisions regarding their pain management options. Our team will discuss all of your treatment choices and what to expect throughout your journey with the foremost pain management doctor in New York . They are here to answer your questions and address your concerns, striving to give you a satisfying experience every time you walk through our doors. Quite simply, they are great at what they do!
Pain Management Specialist
advanced techniques
personalized care

trusted by 4 k+ customers



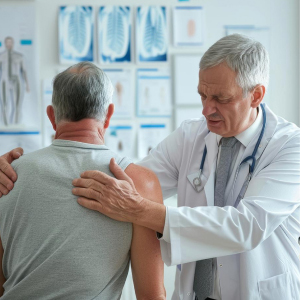

We offer top-quality physiotherapy services tailored to your needs. Our expert therapists use advanced techniques to treat pain, improve mobility.
At Physiocare, we pride ourselves on providing exceptional physiotherapy services that deliver real results. But don't just take our word for it.