A herniated disc, also known as a slipped or ruptured disc, is a common condition that can cause significant pain and discomfort. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and knowing when to seek treatment can be crucial in managing this condition effectively. At DiagnosticSpineCare, we are dedicated to providing comprehensive care for individuals suffering from herniated discs, ensuring they receive the best possible treatment to restore their quality of life.
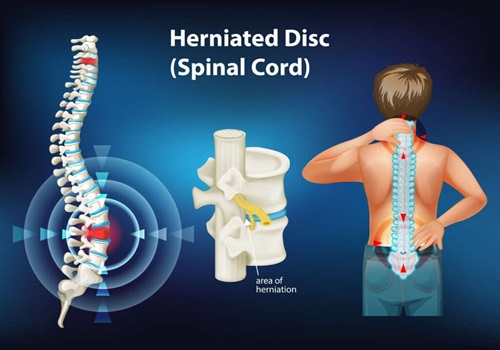
Symptoms of a Herniated Disc
Common Symptoms
The symptoms of a herniated disc can vary depending on the location of the affected disc and the severity of the herniation. However, there are some common symptoms that many patients experience:
- Back Pain and Leg Pain: One of the most common symptoms of a herniated disc is pain in the lower back, which may radiate down the legs. This condition, known as sciatica, occurs when the herniated disc compresses the sciatic nerve. The pain can be sharp, shooting, or burning and may worsen with certain movements or activities.
- Numbness or Tingling: When a herniated disc compresses nearby nerves, it can cause numbness or tingling in the areas served by those nerves. For example, a herniated disc in the lower back may cause numbness or tingling in the legs or feet, while a herniated disc in the neck may affect the arms or hands.
- Muscle Weakness: Muscle weakness is another potential symptom of a herniated disc. This occurs when the compressed nerve affects the muscles that it controls, making it difficult to perform certain tasks or movements. For instance, you might find it challenging to lift objects, walk, or even stand for extended periods.
Emergency Symptoms
While most cases of herniated discs can be managed with non-surgical treatments, there are certain emergency symptoms that require immediate medical attention. These symptoms can indicate severe nerve compression or other complications that, if left untreated, could lead to permanent damage:
- Loss of Bowel or Bladder Control: This symptom is a red flag for a serious condition known as cauda equina syndrome. It occurs when the herniated disc compresses the bundle of nerves at the base of the spine, leading to a loss of control over bowel or bladder functions. This condition is a medical emergency and requires prompt surgical intervention to prevent long-term complications.
- Severe Weakness: If you experience sudden and severe weakness in your legs, it could indicate that the nerves controlling your muscles are being severely compressed. This weakness may make it difficult or impossible to walk, and it requires urgent medical evaluation.
- Intense, Unrelenting Pain: While pain is a common symptom of a herniated disc, intense and unrelenting pain that does not improve with rest or medication can be a sign of a more serious problem. If you experience this type of pain, it’s important to seek medical attention to determine the cause and appropriate treatment.
Causes of a Herniated Disc
Understanding the causes of a herniated disc can help you take steps to prevent this condition and protect your spine health. While a herniated disc can occur in anyone, certain factors can increase your risk:
Degenerative Disc Disease
As we age, the discs in our spine naturally lose some of their water content, making them less flexible and more prone to damage. This condition, known as degenerative disc disease, is a common cause of herniated discs in older adults. Over time, the wear and tear on the discs can cause them to weaken and become more susceptible to herniation.
Injury or Trauma
A sudden injury or trauma to the spine, such as from a car accident, fall, or sports injury, can cause a herniated disc. The force from the impact can cause the disc to rupture or bulge, leading to pain and other symptoms. Even a seemingly minor injury can result in a herniated disc, especially if the spine is already weakened from degenerative changes.
Repetitive Strain
Repetitive movements that place stress on the spine, such as heavy lifting, twisting, or bending, can increase the risk of a herniated disc. Jobs that require physical labor or activities that involve repetitive motions, such as construction work or certain sports, can put added strain on the spine and contribute to disc herniation over time.
Genetic Factors
Genetics may increase the risk of herniated discs by making spinal discs more prone to damage. If you have a family history of spine conditions, you may be more prone to developing a herniated disc. Certain genetic factors can affect the strength and flexibility of your discs, making them more susceptible to injury and degeneration.
When to Seek Emergency Care
Recognizing the red flags that indicate a medical emergency is crucial when dealing with a herniated disc. While many cases can be managed with conservative treatments, certain symptoms require immediate medical attention to prevent permanent damage:
Understanding the Red Flags
- Loss of Bowel or Bladder Control: As mentioned earlier, this symptom can indicate cauda equina syndrome, a serious condition that requires emergency surgery. If you experience a sudden inability to control your bowel or bladder, seek medical attention immediately.
- Severe Muscle Weakness: Sudden and severe weakness in your legs or arms can be a sign of nerve compression that could lead to permanent muscle damage. If you are unable to move your limbs or if you experience a significant loss of strength, it’s important to seek medical care right away.
- Unrelenting Pain: If you experience pain that does not improve with rest or medication and becomes unbearable, it could be a sign of a more serious problem. Persistent, intense pain should never be ignored, as it could indicate a severe herniation or other complications.
Why Early Intervention is Critical
Early intervention is key to preventing long-term complications from a herniated disc. In some cases, delaying treatment can lead to permanent nerve damage, chronic pain, or loss of function. Seeking prompt medical care when you experience emergency symptoms can help ensure that you receive the appropriate treatment to avoid these complications.
Treatment Options for a Herniated Disc
At DiagnosticSpineCare, we offer a range of treatment options for herniated discs, tailored to meet the unique needs of each patient. The goal of treatment is to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and restore normal function to the affected area.
Non-Surgical Treatments
For many patients, non-surgical treatments are effective in managing the symptoms of a herniated disc. These treatments focus on relieving pain, reducing inflammation, and promoting healing:
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy is often the first line of treatment for a herniated disc. A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to strengthen the muscles surrounding the spine, improve flexibility, and reduce pressure on the affected disc. Stretching and strengthening exercises can also help alleviate pain and prevent future injuries.
- Medication: Pain and inflammation can be managed with over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen. In some cases, prescription medications, such as muscle relaxants or stronger painkillers, may be necessary to manage more severe symptoms.
- Epidural Steroid Injections: If pain persists despite other treatments, an epidural steroid injection may be recommended. This procedure involves injecting a corticosteroid directly into the epidural space around the affected nerve, reducing inflammation and relieving pain. The effects of the injection can last for several weeks or months, providing relief while the disc heals.
Surgical Treatments
When non-surgical treatments are not effective, or when there is severe nerve compression, surgery may be necessary to relieve the symptoms of a herniated disc:
- Microdiscectomy: Microdiscectomy is a minimally invasive surgery that involves removing the herniated portion of the disc to relieve pressure on the affected nerve. This procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia and involves making a small incision in the back to access the disc. Most patients experience significant pain relief following the surgery and can return to normal activities within a few weeks.
- Laminectomy: In some cases, a laminectomy may be performed to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves. This procedure involves removing a portion of the vertebral bone, called the lamina, to create more space for the nerves. A laminectomy is often combined with a microdiscectomy to address both the herniated disc and any bone spurs or other structures that may be compressing the nerves.
Alternative Therapies
In addition to traditional treatments, some patients find relief from alternative therapies that focus on holistic and non-invasive approaches to pain management:
- Chiropractic Care: Chiropractic care involves spinal adjustments and manipulations to realign the spine and reduce pressure on the affected disc. Many patients find that chiropractic adjustments help relieve pain and improve mobility, especially when combined with other treatments like physical therapy.
- Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese therapy involves placing thin needles at specific body points to promote healing and alleviate pain. Some studies have shown that acupuncture can be effective in managing chronic back pain, including pain caused by a herniated disc.
Lifestyle Changes and Prevention
Preventing a herniated disc or managing its symptoms involves making certain lifestyle changes that promote spine health and reduce the risk of further injury. Here are key areas to focus on:
- Ergonomics
Proper posture and workplace ergonomics play a crucial role in preventing herniated discs. Whether you’re sitting at a desk, driving, or lifting objects, maintaining correct posture can significantly reduce strain on your spine. Use ergonomic chairs and desks that support the natural curve of your spine, and make sure your workstation is set up to minimize repetitive strain.
- Exercise
Regular exercise is vital for strengthening the muscles that support your spine, particularly the back and core muscles. A well-balanced exercise routine that includes stretching, strengthening, and aerobic activities can help maintain spine flexibility and prevent disc problems. Exercises like planks, bridges, and gentle yoga can be particularly beneficial in supporting spinal health.
- Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for reducing stress on your spine. Excess weight, especially around the midsection, can shift your center of gravity and put extra pressure on the lower back, increasing the risk of a herniated disc. A balanced diet combined with regular physical activity can help you achieve and maintain a healthy weight, thereby supporting overall spine health.
Conclusion
Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for herniated discs is crucial for managing this condition effectively. Whether you are experiencing mild discomfort or severe pain, early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can make a significant difference in your recovery and long-term spine health.
At DiagnosticSpineCare, we are committed to providing personalized treatment plans that address your unique needs and help you return to a pain-free life. Our team of experts is dedicated to offering the most effective and minimally invasive treatments available, ensuring you receive the highest standard of care.
Call to Action
If you or a loved one are struggling with the symptoms of a herniated disc, don’t wait to seek professional help. Contact DiagnosticSpineCare today to schedule a consultation and learn more about the treatment options that are right for you.
Visit our website for more information on our services, or call us to book an appointment with our experienced team. Take the first step towards a pain-free life with expert care from DiagnosticSpineCare.
